
There are 85,000 new malicious IPs launched every day and the top phishing targets are technology companies and financial institutions.
These are among the findings of a new report from threat intelligence and security company Webroot. The Webroot 2015 Threat Brief provides the latest cyber threat trends collected from tens of millions of users and over 30 security technology partners.
The report finds that the United States accounts for 31 percent of malicious IP addresses, followed by China with 23 percent and Russia with 10 percent. Overall, half of malicious IP addresses are based in Asia.
It shows a 30 percent chance of Internet users falling for a zero-day phishing attack in the course of a year, and indicate a more than 50 percent increase in phishing activity in December 2014, most likely due to the holiday season.
On average, there are nearly 900 phishing attempts detected per financial institution, but over 9,000 attempts detected per technology company. The top five technology companies impersonated by phishing sites are: Google, Apple, Yahoo, Facebook and Dropbox. Looked at by country, the US is by far the largest host of phishing sites, with over 75percent being within its borders.
Looking at mobile systems the report finds that, on average, only 28 percent of apps on the Android platform were trustworthy or benign, a drop from 52 percent in 2013. Almost half were rated were moderate or suspicious, and over 22 percent were unwanted or malicious. Trojans make up the vast majority of malicious threats, averaging 77 percent for 2014.
"Webroot has seen a continued rise in the number of malicious URLs, IP addresses, malware, and mobile applications used to enable cybercriminals to steal data, disrupt services, or cause other harm," says Hal Lonas, chief technology officer at Webroot. "With more breaches at major retailers, financial institutions and technology companies in the headlines and scores of other, smaller breaches in 2014, the trend shows no signs of slowing down. The Webroot 2015 Threat Brief highlights the need for highly accurate and timely threat intelligence to help organizations assess the risk of incoming data, reduce the volume of security incidents, and accelerate response to successful attacks".
2014 has also seen more sophisticated techniques being used to attack PCs. These include the Poweliks registry exploit which doesn't require extra components to deliver infections like ransomware. Webroot also discovered five new families of potentially unwanted application, each demonstrating new social engineering techniques and complexity.
The full report is available as a PDF from the Webroot site and there's a summary of the findings in infographic form below.
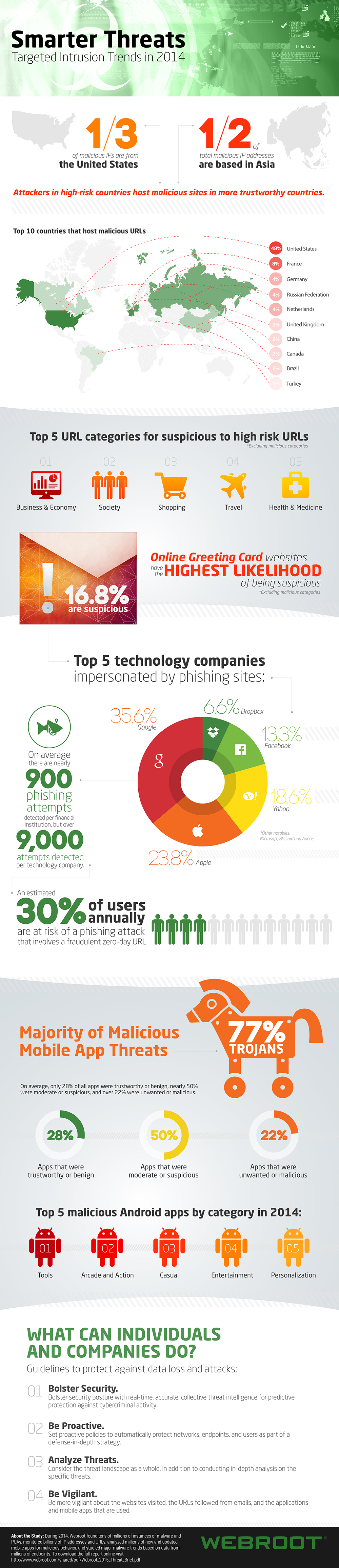
Photo Credit: ra2studio / Shutterstock

